The test case shows how to achieve minimum patch size by doing ECO in two steps.
The ECO case has two changes in RTL codes. Both of them are modifications of complicated combinational signal.
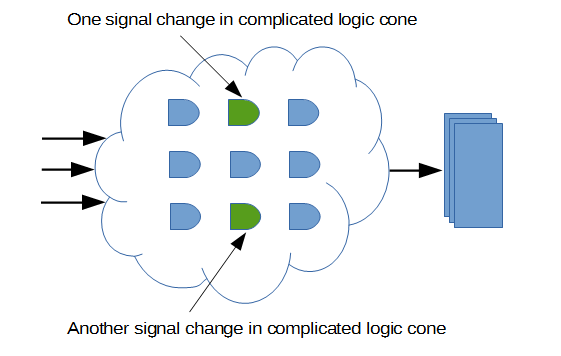
Figure 1: Changes for two complicated combinational signals
It's hard to find the exact ECO locations by manual way. However, if the two changes are fixed at the same time by automatic tool, the patch size is big and some redundant logics are added.
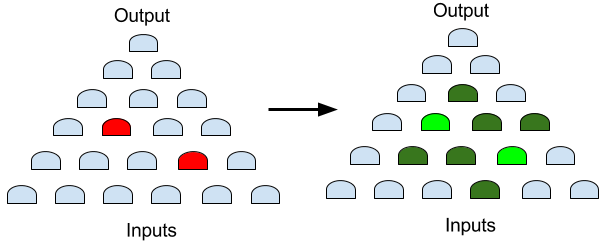
Figure 2: Fix two changes in one shot
GOF uses two steps to fix the two changes and achieves the minimum patch size.
The step one is to fix one signal in RTL and run synthesis to generate Reference Netlist One. Implementation Netlist is fixed by referencing Reference Netlist One and Middle Neltist is generated after the step one ECO.
The step two is to fix the other signal in RTL and run synthesis to generate Reference Netlist Two. Middle Netlist generated in the step one is fixed by referencing Reference Netlist Two and the final ECOed Netlist is generated after the step two ECO.
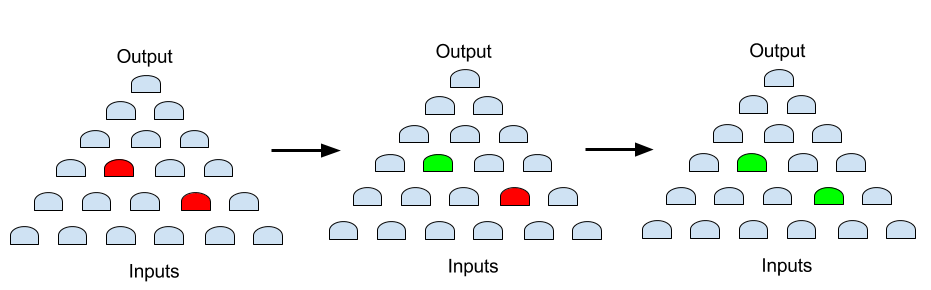
Figure 3: Two steps ECO
Conformal ECO can't yield good result by two steps ECO, due to its fundamental defect in handling complicated combinational signal ECO. Check this link for more detail, "GOF vs Conformal ECO".
# GofCall ECO script, eco_step1.gpl use strict; undo_eco; # Discard previous ECO operations setup_eco("eco_step1"); # Setup ECO name read_library("m28.lib"); # Read in standard library # Read in the Reference Netlist which is re-synthesized with several modules modified read_design("-ref", "ref_step1.v"); # Read in the implementation Netlist Which is under ECO read_design("-imp", "imp.v"); set_top("top"); # Set the top module set_ignore_output("cshi_so*"); # To avoid test lockup to affect the ECO result set_pin_constant("cshi_se",0); # To avoid test logic being touched fix_design; report_eco(); # ECO report write_verilog("eco_middle.v"); # Write out ECO result in Verilog exit;
# GofCall ECO script, eco_step2.gpl use strict; undo_eco; # Discard previous ECO operations setup_eco("eco_step2"); # Setup ECO name read_library("m28.lib"); # Read in standard library # Read in the Reference Netlist which is re-synthesized with several modules modified read_design("-ref", "ref_step2.v"); # Read in the netlist generated in Step One ECO read_design("-imp", "eco_middle.v"); set_top("top"); # Set the top module set_ignore_output("cshi_so*"); # To avoid test lockup to affect the ECO result set_pin_constant("cshi_se",0); # To avoid test logic being touched fix_design; report_eco(); # ECO report write_verilog("eco_final.v"); # Write out ECO result in Verilog exit;
Three experiments have been run on the ECO case. The results are,
| ECO Result | Total Cells | Area |
| Conformal ECO | ~65 | 35.3 |
| GOF (In one shot) | 82 | 34.2 |
| GOF (in two steps) | 3 | 2.9 |
The files can be downloaded to reproduce the result
The Step One ECO Command:
gof -lib m28.lib imp.v -ref ref_step1.v -run eco_step1.gpl
The Step Two ECO Command:
gof -lib m28.lib eco_middle.v -ref ref_step2.v -run eco_step2.gpl
Two steps ECO can fully utilize the Logic Optimization Algorithm of Gates On the Fly.