RTL-guided ECO without re-synthesis eliminates the need for a full synthesis run, which is typically the most time-consuming step in the ECO flow. In many cases, RTL changes introduced during an ECO are incremental and do not justify re-running synthesis from scratch. GOF addresses this challenge by enabling ECO changes to be applied directly to the implementation netlist, bypassing re-synthesis entirely. As a result, ECOs on multi-million-gate netlists can be completed in as little as 20 minutes, compared to several days with a traditional re-synthesis-based approach.
In this flow, only the original RTL, the modified RTL, and the implementation netlist are required. GOF analyzes the differences between the reference RTL and the modified RTL, automatically generates the corresponding ECO operations, and applies them to the implementation netlist. This approach significantly reduces ECO turnaround time and engineering effort, resulting in a faster and more efficient ECO implementation.
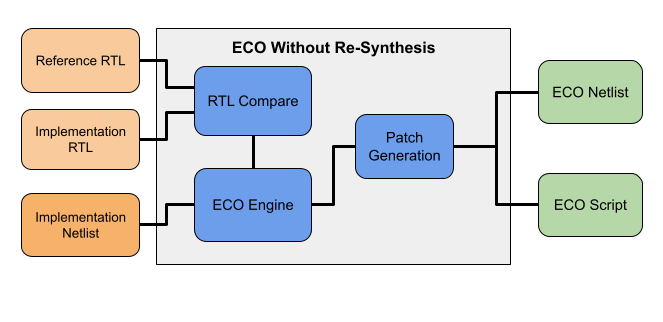
Figure 1: RTL Guided ECO Without Re-Synthesis
This method is particularly well suited for small to medium-sized ECOs, where design changes are localized and do not impact the overall structure of the design. By leveraging GOF’s robust RTL comparison, netlist analysis, and ECO generation capabilities, designers can rapidly implement functional changes without the overhead of a full synthesis flow.
Best practice is to apply the ECO to the pre-layout netlist first. The resulting ECO script can then be reused to update the DFT netlist and the post-layout netlist. This staged approach helps avoid boundary optimization and logic restructuring issues that often arise when ECOs are applied directly to post-layout netlists.
RTL Guided ECO without re-synthesis example script:
# GOF ECO script, rtl_eco_wo_syn.pl use strict; setup_eco("rtl_eco_wo_syn_example");# Setup ECO name read_library("art.5nm.lib");# Read in standard library set_define("SYNTHESIS"); set_define("NO_SIM"); set_inc_dirs("/project/nd900/vlib/include", "/project/nd900/IPS/include"); read_rtl('-ref', "ref0.sv", "ref1.sv", "ref2.sv"); read_rtl('-imp', "imp0.sv", "imp1.sv", "imp2.sv"); set_top("topmod"); rtl_compare(); read_svf("-imp", "syn.svf.txt"); # Optional, must be loaded before read_design, must be in text format read_design("-imp", "prelayout.gv");# Read in Implementation Netlist Which is under ECO set_top("topmod");# Set the top module # Preserve DFT Test Logic set_ignore_output("scan_out*"); set_pin_constant("scan_enable", 0); set_pin_constant("scan_mode", 0); fix_design(); report_eco(); # ECO report check_design();# Check design for issues such like floating write_perl("eco_wo_syn.pl");# Write out ECO result to Perl script write_verilog("eco_verilog.gv");# Write out ECO result in Verilog exit; # Exit when the ECO is done, comment it out to go to interactive mode when 'GOF >' appears
After generating the ECO Perl script, it can be applied to the DFT and post-layout netlists.
Applying the ECO script to the post-layout netlist:
use strict; setup_eco("apply_script_pre2post");# Setup ECO name read_library("art.5nm.lib");# Read in standard library read_design("-imp", "postlayout.gv");# Read in Implementation Netlist Which is from backend set_top("topmod"); run("eco_wo_syn.pl"); write_verilog("postlayout_eco.gv"); exit;
In many scenarios, it is unnecessary to provide the full RTL for comparison. If the ECO impacts only a specific sub-module, GOF can limit the RTL comparison to that module. Designers can specify the hierarchical instances to be updated using set_path_prefix.
For example, if the RTL modification affects SUB_MOD_A, and the change needs to be applied to two instances 'u_sub_mod1/u_sub_mod_a' and 'u_sub_mod3/u_sub_mod_a_1' only the sub-module RTL files are required. GOF applies the ECO selectively to the specified hierarchical paths.
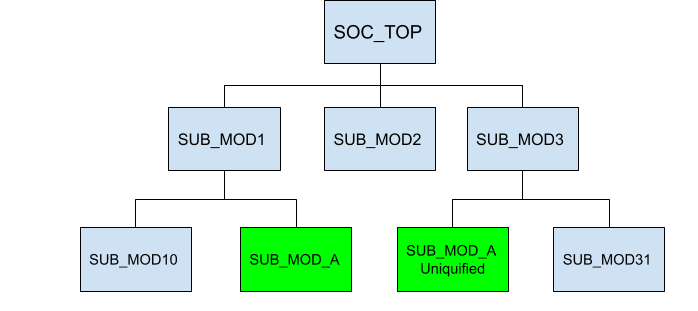
Figure 2: RTL Compare on Sub-module
RTL guided ECO with sub-module only:
# GOF ECO script, rtl_eco_wo_syn.pl use strict; setup_eco("rtl_on_sub_mod");# Setup ECO name read_library("art.5nm.lib");# Read in standard library set_path_prefix("u_sub_mod1/u_sub_mod_a", " u_sub_mod3/u_sub_mod_a_1"); read_rtl('-ref', "SUB_MOD_A.modified.v"); read_rtl('-imp', "SUB_MOD_A.v"); set_top("SUB_MOD_A"); rtl_compare(); read_svf("-imp", "syn.svf.txt"); # Optional, must be loaded before read_design, must be in text format read_design("-imp", "prelayout.gv");# Read in Implementation Netlist Which is under ECO set_top("SOC_TOP");# Set the top module # Preserve DFT Test Logic set_ignore_output("scan_out*"); set_pin_constant("scan_enable", 0); set_pin_constant("scan_mode", 0); fix_design(); report_eco(); # ECO report check_design();# Check design for issues such like floating write_perl("eco_wo_syn.pl");# Write out ECO result to Perl script write_verilog("eco_verilog.gv");# Write out ECO result in Verilog exit; # Exit when the ECO is done, comment it out to go to interactive mode when 'GOF >' appears
RTL-guided ECO without re-synthesis is an efficient and scalable approach for implementing functional ECOs with minimal turnaround time. By directly comparing original and modified RTL and applying the resulting changes to the implementation netlist, GOF enables fast, controlled, and repeatable ECO execution. The ability to scope ECOs down to specific sub-modules further enhances productivity, making this flow especially effective for localized design updates late in the design cycle.