Conformal ECO does not perform well with boundary optimized netlists from Design Compiler Topographical (DCT) mode synthesis. It adds more gates than necessary in the DCT/DCG netlist ECO.
Synopsys Design Compiler Topographical (DCT) and Design Compiler Graphical (DCG) are tools that optimize netlists for floorplanning, routing, and timing. However, they can make functional ECO more difficult. During synthesis, they can change hierarchical module boundaries to add clone ports or invert the original ports' phase and merge flops.
Conformal ECO has issues with ports mapping in functional ECO. As shown in Figure 1, Conformal ECO incorrectly maps the clone ports added by DCG/DCT, resulting in three times more gates being used than necessary to fix the logic.
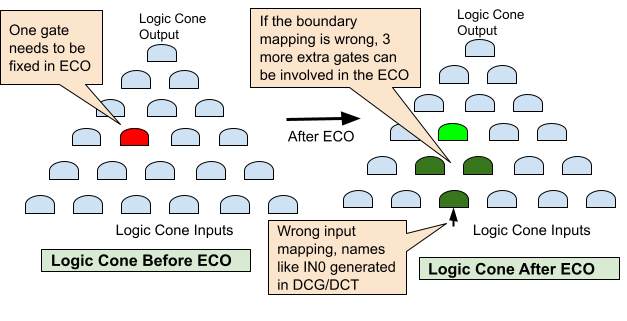
Figure 1: Boundary mapping affects ECO quality
The synthesis tool adds cloned ports that do not have a one-to-one mapping between the Reference Netlist and the Implementation Netlist. When the ECO tool attempts to make these ports equal, it can result in redundant gates being added to the ECO patch or even make the final logic not equivalent.
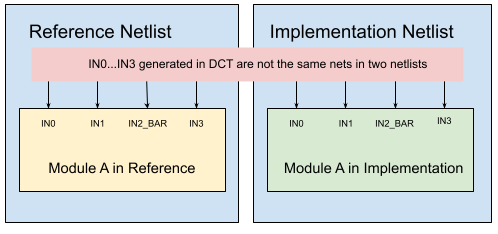
Figure 2: DCG/DCT Boundary optimized netlist
However, GOF is able to map the clone ports correctly, ensuring that only the exact non-equivalent point is fixed.
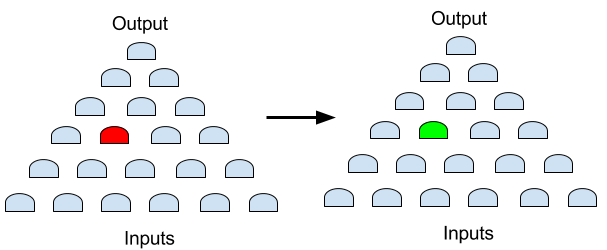
Figure 3: GOF result, only the red spot is fixed
Read more on GOF vs Conformal ECO